Seoul Forest
Opened in 2005, Seoul Forest (서울숲; map) is Seoul’s third largest park, behind Olympic Park and World Cup Park. Measuring 1.2-square-kilometers, it sits in the Seongsu Neighborhood, bordering Jungnang Stream (중랑천; map) and the Han River.
Today, Seoul Forest hosts an abundance of green branches, silver-topped reeds, and sculptures. But the land where it sits holds a deep history.
- Seoul Forest sat outside the fortress walls of Hanseong, the capital of the Joseon Dynasty (1392~1897). Kings used the area as the hunting grounds and military training fields.
- The area held Seoul’s first water treatment facility (수도박물관; map). Completed in 1908, the plant purified water for 165,000 Seoul residents; about 32% of the population. Its main building still sits in Seoul Forest.
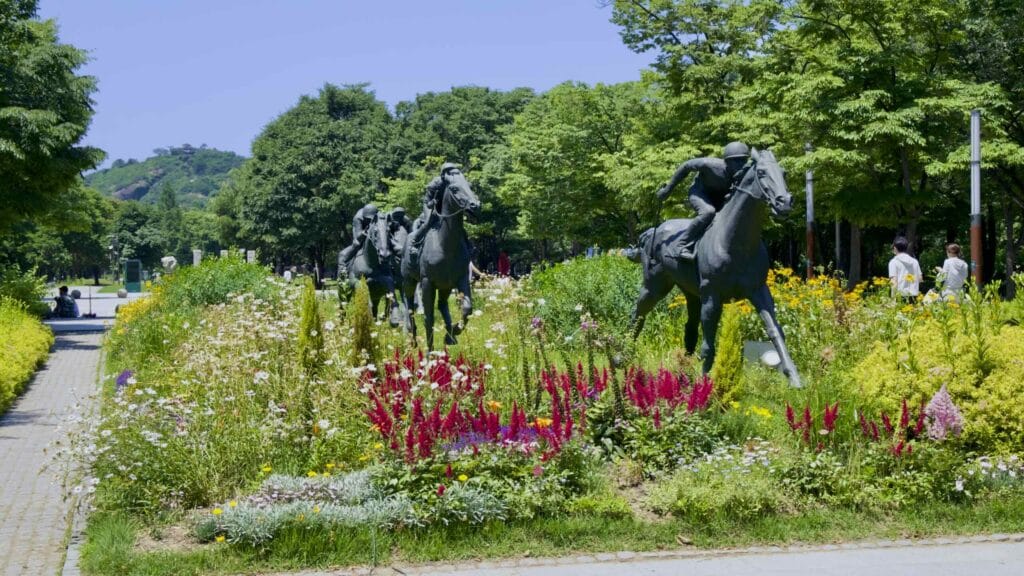
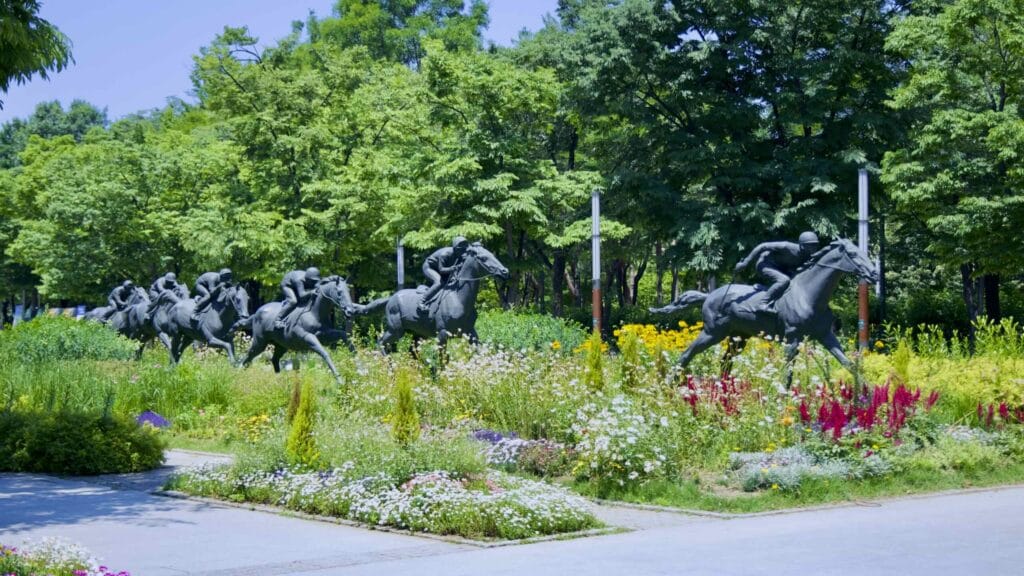
- From 1954 to 1989, Seoul Forest hosted the city’s first horse racetrack, which included a small golf course in the infield. You can see racehorse statues in Seoul Forest’s entrance plaza.
Planners divided Seoul Forest into five sections. Each sports unique characteristics.
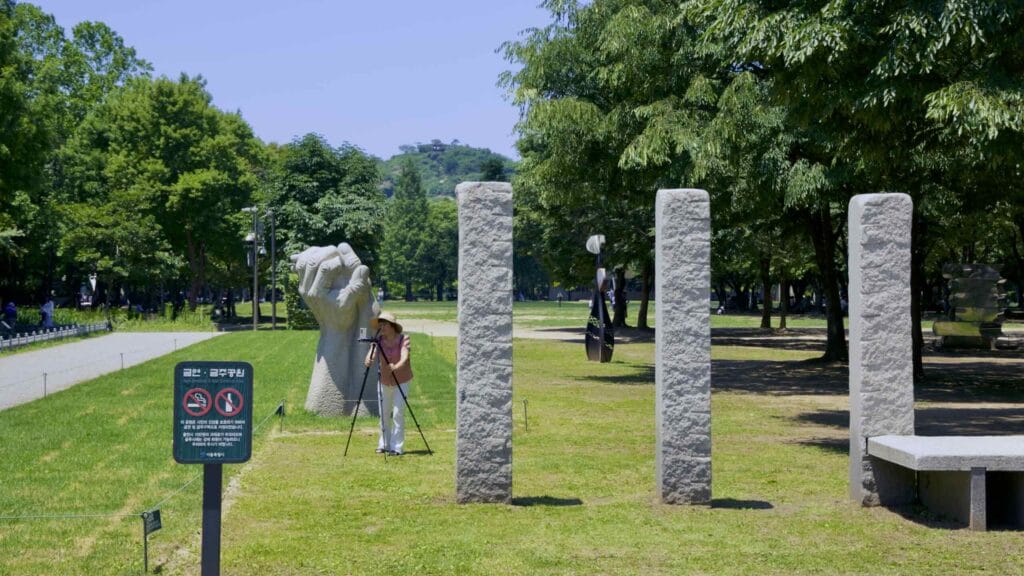
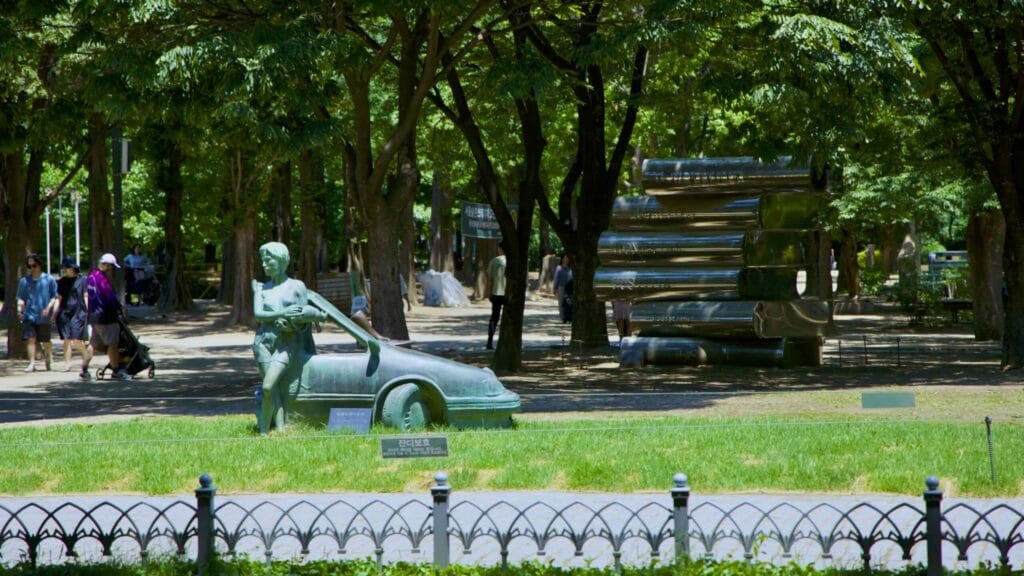
- Culture & Arts Park — plaza, visitors center, and sculptures.
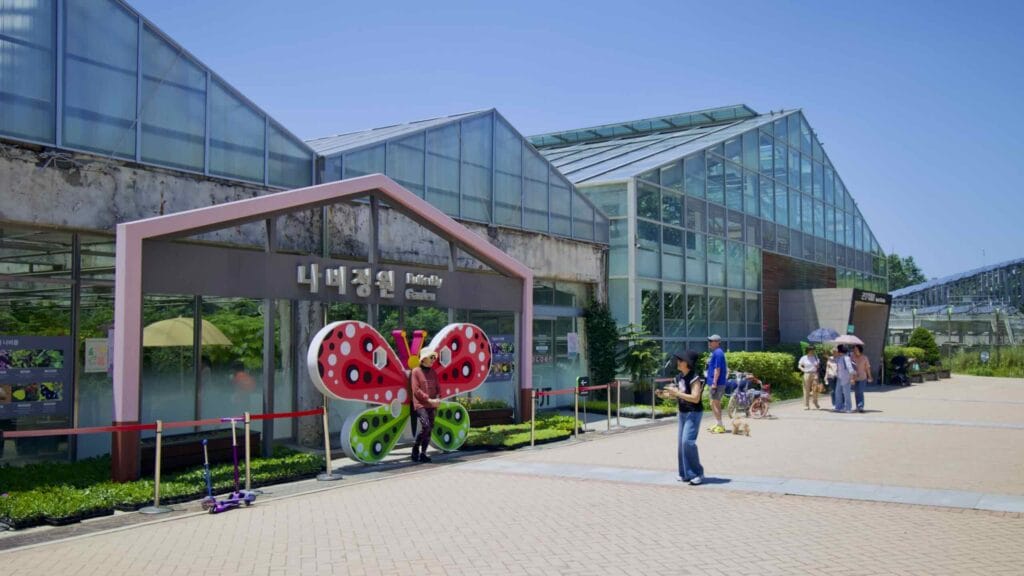
- Experience Learning Center — old water treatment plant, insect and flower gardens.
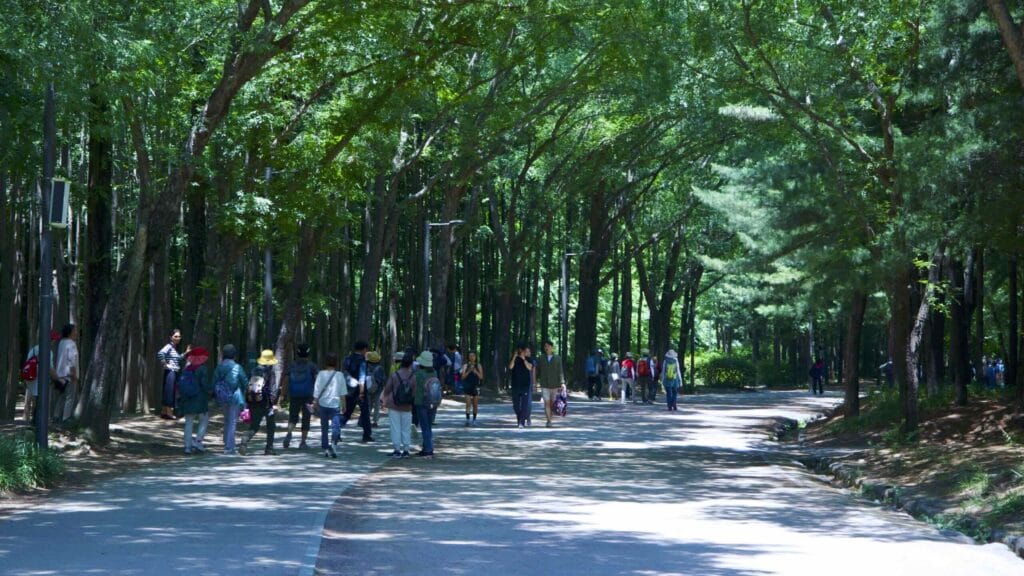
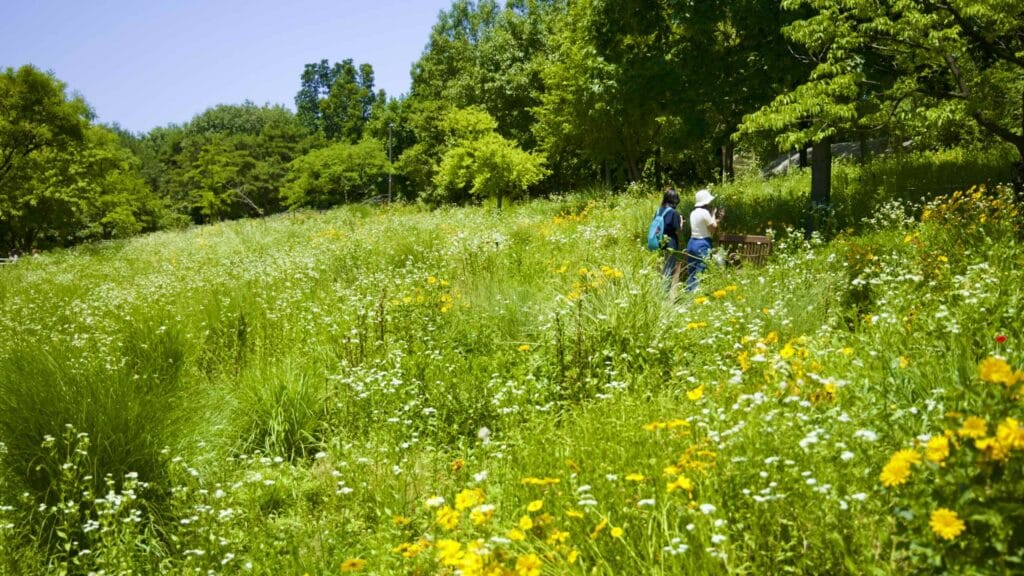
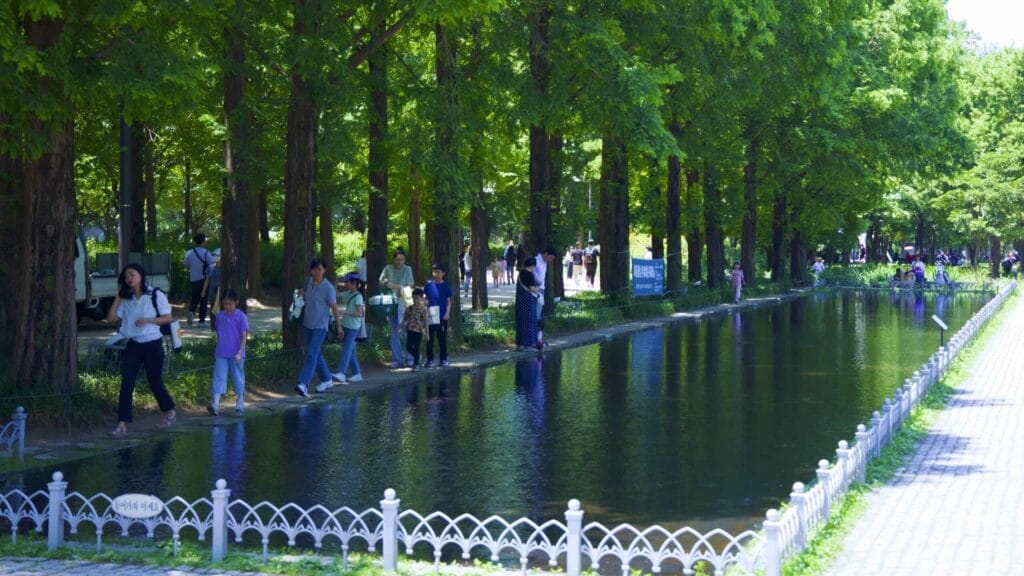
- Eco Forest — plentiful trees, walking paths, and a small zoo.
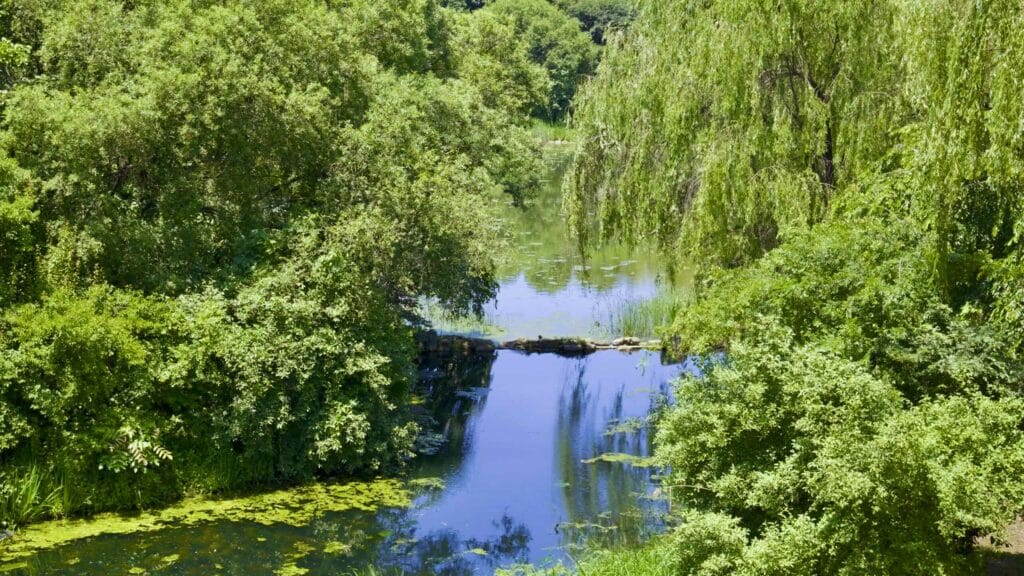
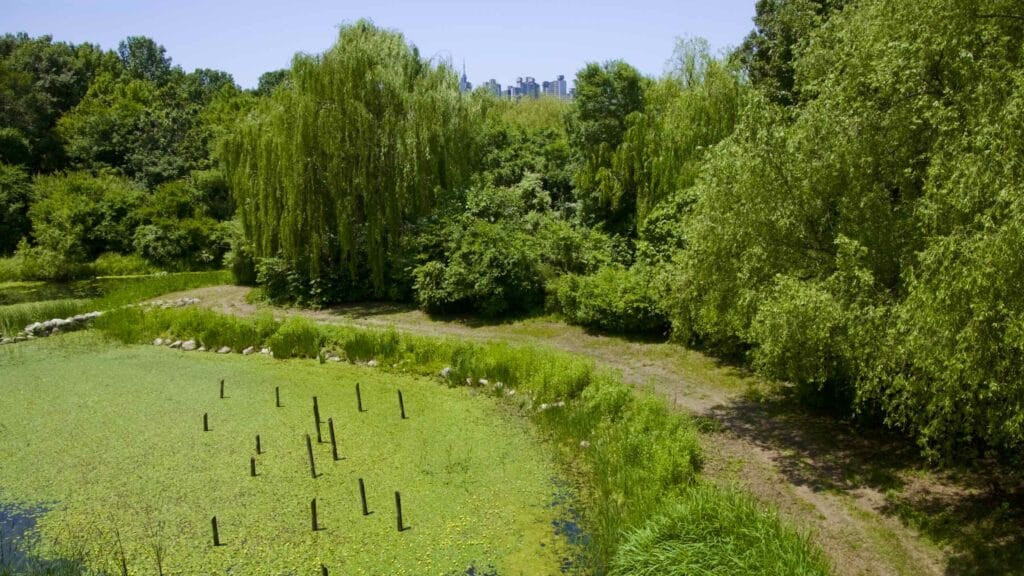
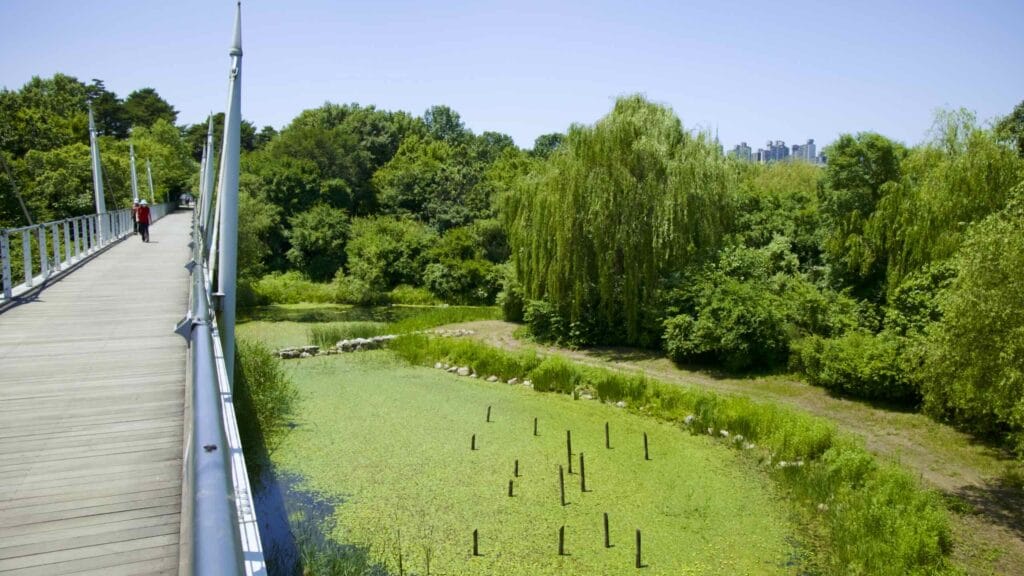
- Wetland Ecology Garden — bird observatory and wetlands gardens.
- Hangang Riverside Park — riverside area with bike paths and marina.

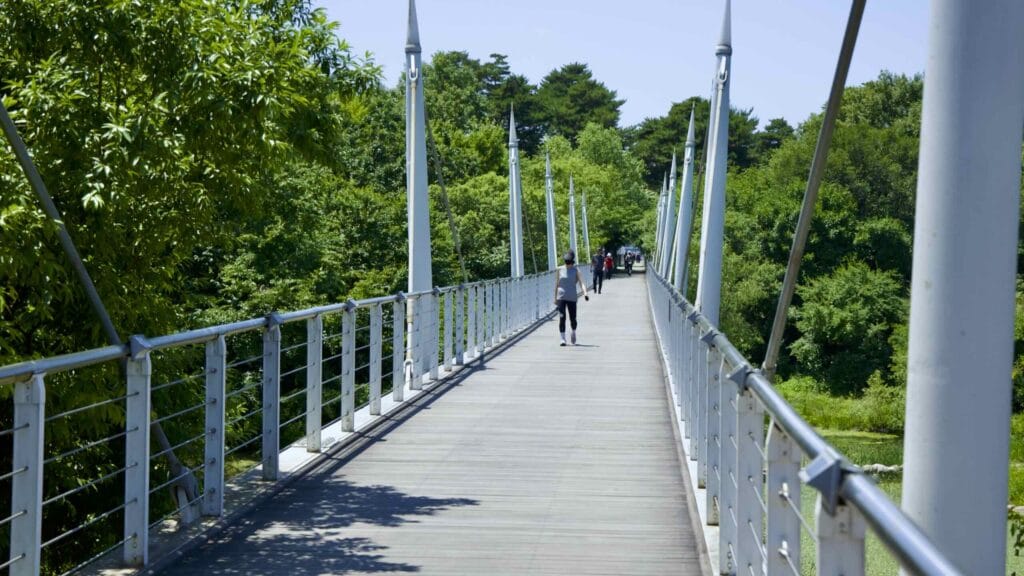
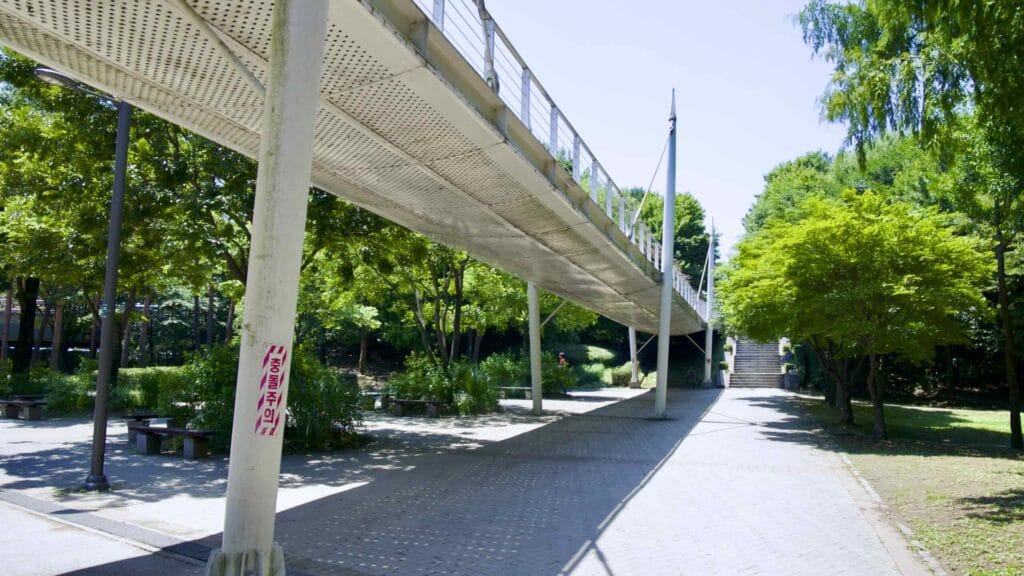
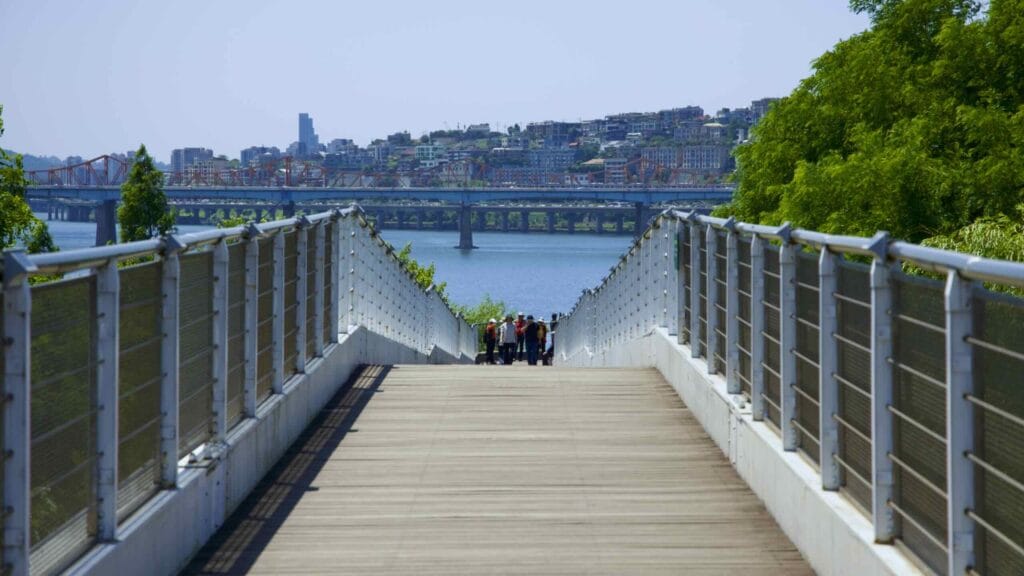
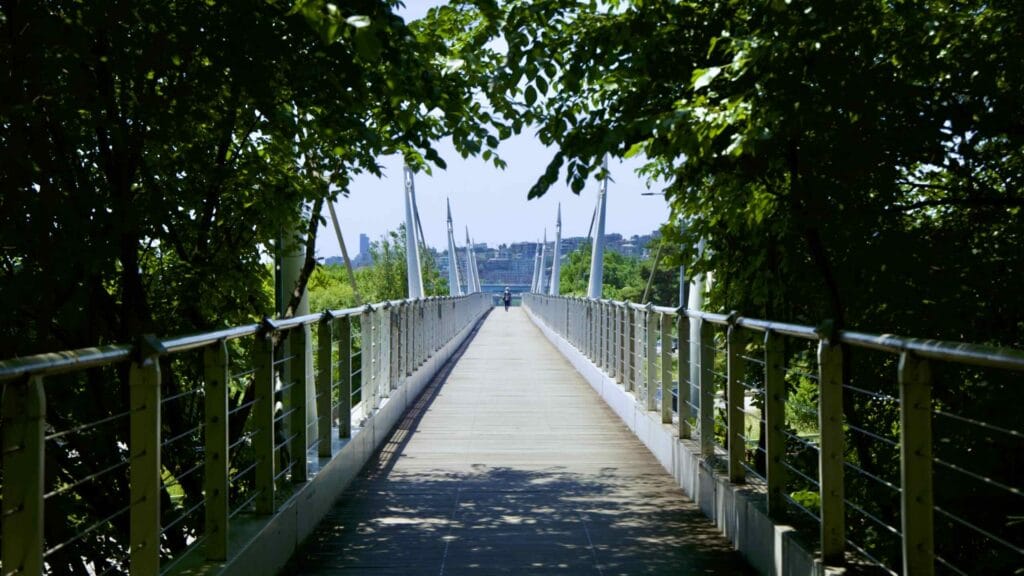
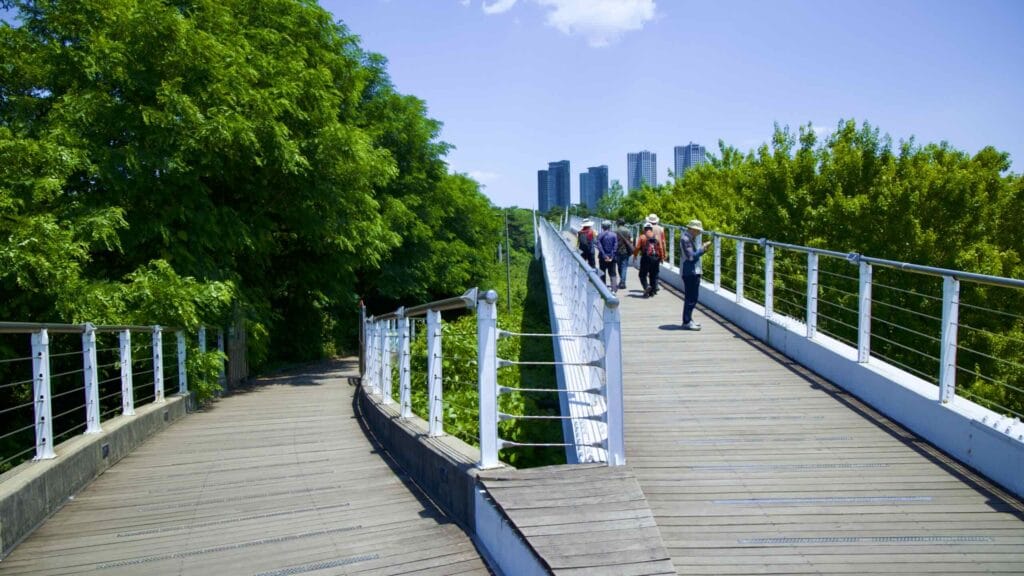
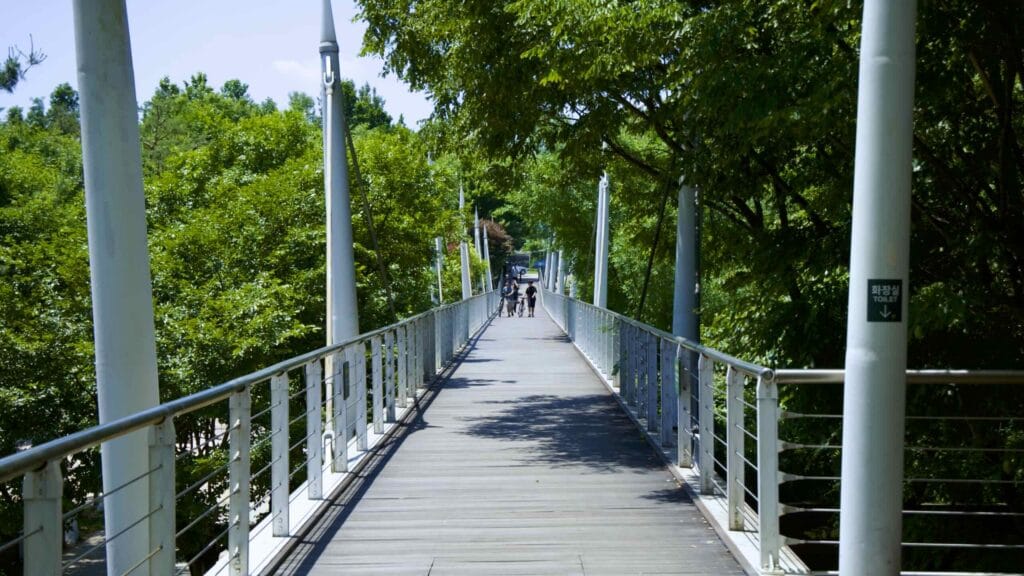
The park also features the Seoul Forest Walk Observatory (서울숲보행전망교; map; aerial view). The pedestrian overpass hovers several meters off the forest floor and passes over the park’s southeast corner.
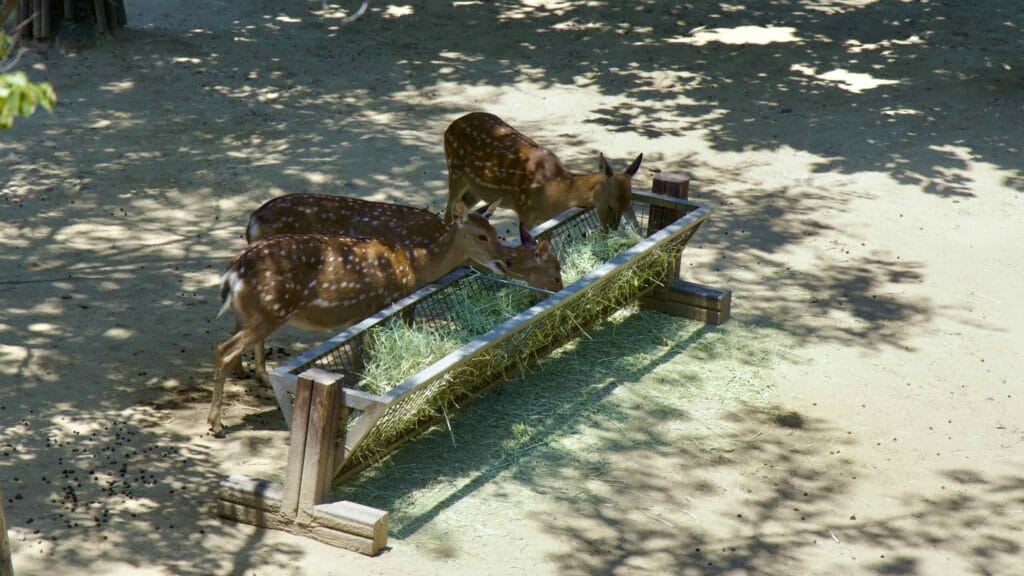
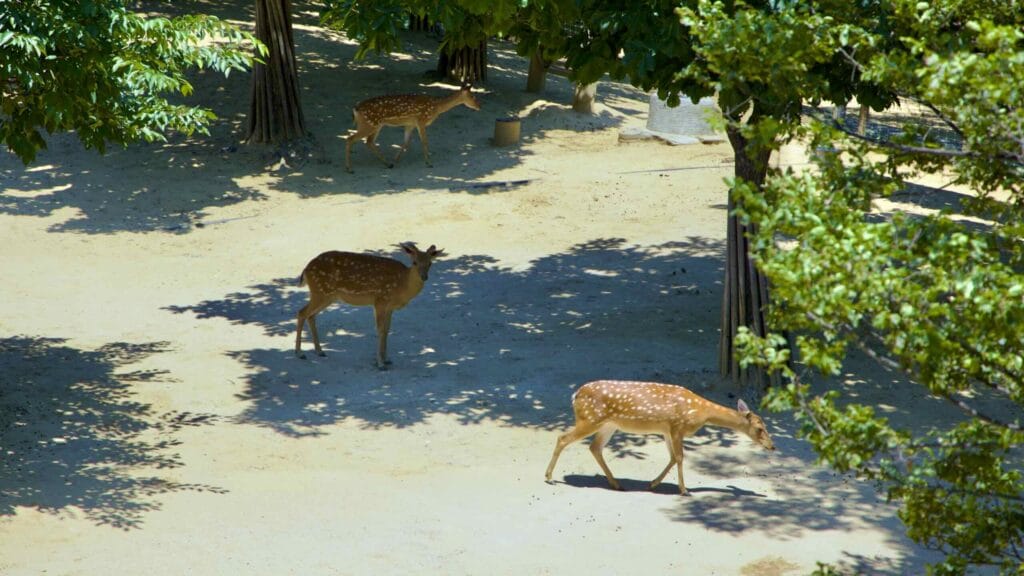
Walk down it and you can spot a fenced off section full of sika deer, boggy ponds, and Windy Hill, Seoul Forest’s highest point.
Seoul Forest Walk Observatory continues out of the park and across Gangbyeon Expressway. It ends in Ttukseom Hangang Park along the Han River and Hangang Bike Path.